

But you should avoid amending commits that have already been made public. !!Note!!: fixing up a local commit with amend is great and you can push it to a shared repository after you've fixed it. Git commit -amend allows you to modify and add changes to the most recent commit.
#Linux command cheat sheet how to#
How to amend the most recent commit in Git: You can use the -p option flag to specify the changes you want to reset. How to revert unstaged changes in Git: git checkout filename This command stages the changes, then it expects a commit message. This command expects a commit message to explain why the file was deleted. How to remove tracked files from the current working tree in Git: This command opens a prompt and asks if you want to stage changes or not, and includes other options.

We can call diff with the -staged flag to see any staged changes. Git diff shows only unstaged changes by default. You can pass a file as a parameter to only see changes on a specific file. How to see changes made before committing them using "diff" in Git:

This command will cause the Git log to show some statistics about the changes in each commit, including line(s) changed and file names. Replace commit-id with the id of the commit that you find in the commit log after the word commit. This command shows the commit's history including all files and their changes: git log -p How to see your commit history including changes in Git: This command shows the commit history for the current repository: git log git commit -a -m"your commit message here" You can add and commit tracked files with a single command by using the -a and -m options. How to commit changes (and skip the staging area) in Git: This command lets you only specify a short summary for your commit message. You can add a commit message without opening the editor. How to commit changes with a message in Git:
#Linux command cheat sheet full#
This command will open a text editor in the terminal where you can write a full commit message.Ī commit message is made up of a short summary of changes, an empty line, and a full description of the changes after it. How to commit changes in the editor in Git: This command will show the status of the current repository including staged, unstaged, and untracked files. How to check a repository's status in Git: With the asterisk in the command below, you can add all files starting with 'fil' in the staging area.
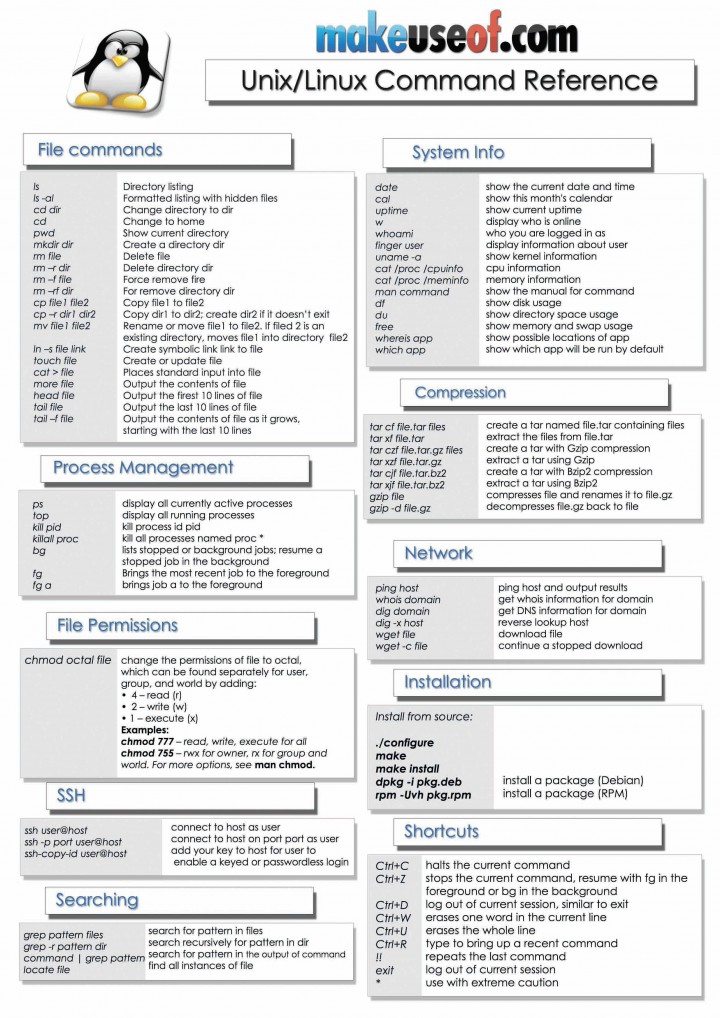
How to add only certain files to the staging area in Git If you want to add all files in your project to the staging area, you can use a wildcard. How to add all files in the staging area in Git Just replace filename_here with the name of the file you want to add to the staging area. The command below will add a file to the staging area. How to add a file to the staging area in Git: You can do so with the command below: git init The first step is to initialize a new Git repo locally in your project root. Just use this command: git config -global credential.helper cacheĮverything starts from here. You can store login credentials in the cache so you don't have to type them in each time. git config -global user.email to cache your login credentials in Git: This command lets you setup the user email address you'll use in your commits. With the command below you can configure your user name: git config -global user.name "Fabio" The command below returns a list of information about your git configuration including user name and email: git config -l So I have written them down and thought it'd be nice to share them with the community. And I've found that these fifty are the ones I use the most often (and are therefore the most helpful to remember). Git has many different commands you can use. This way, different members of the team can copy it locally and everyone has a clear overview of all changes made by the whole team. Then, thanks to an external server like BitBucket, GitHub or GitLab, they can safely store the repository in a single place. Everyone on the team can keep a full backup of the repositories they're working on on their local machine. This change history lives on your local machine and lets you revert to a previous version of your project with ease in case something goes wrong. What is a Distributed Version Control System?Ī distributed version control system is a system that helps you keep track of changes you've made to files in your project. Linus Torvalds, the developer of the Linux kernel, created Git in 2005 to help control the Linux kernel's development. Git is a distributed version control system that helps developers collaborate on projects of any scale.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
